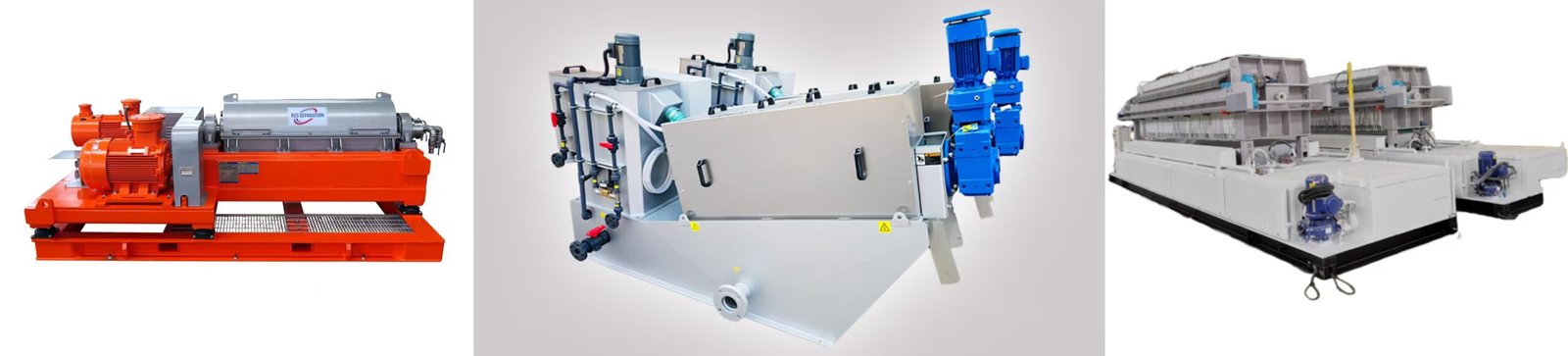
Similarities
These three types of equipment are all used for solid-liquid separation in industrial processes and are widely used in wastewater treatment, chemical manufacturing, food production, and pharmaceutical industries. Their primary objective is to minimize waste while maximizing the efficiency of separating liquids and solids, whether to achieve dewatering or recover reusable materials. By incorporating advanced automation, they streamline operations, reduce labor requirements, and enhance overall productivity.
Differences
| Decanter Centrifuge | Screw Press | Filter Press | |
| Working Principle | Solid-liquid separation is achieved through high-speed rotation centrifugal force. | Uses a screw shaft to apply pressure and gaps for dewatering. | Forces solid-liquid separation using filter cloths and a pressurized system. |
| Applicable Scenarios | Suitable for handling mixtures with high solid content and small particles, such as sludge and suspensions. | Ideal for low to medium solid content sludge, especially oily or organic sludge. | Commonly used for high solid content, high-viscosity mixtures such as slurry or industrial wastewater. |
| Processing Capacity | Large processing capacity, suitable for continuous operation. | Relatively smaller capacity, ideal for medium to small-scale sludge treatment. | Large capacity but requires intermittent operation. |
| Dewatering Effectiveness | Good dewatering effect, suitable for high-precision separation. | Moderate dewatering effect, low energy consumption, with relatively higher solid moisture content post-treatment. | Best dewatering performance with the lowest solid moisture content. |
| Footprint | Small footprint | Compact | Larger footprint |
| Energy Consumption | High energy consumption, requiring significant power support. | Low energy consumption and cost-effective. | Moderate energy consumption, relying on hydraulic or mechanical pressing. |
| Summary | Suitable for large volumes and high-precision separation, high level of automation, relatively high investment cost. | More energy-efficient, suitable for medium to small-scale sludge treatment but with moderate dewatering efficiency. | Offers the best dewatering effect, ideal for high-solid-content scenarios, but operates intermittently and requires more space. |
